

Therefore the domain of ( q ∘ p ) is the set of all real numbers. ( q ∘ p ) ( x ) = q ( p ( x ) ) Def'n of compos. Step 2: Find ( q ∘ p ) ( x ) and its domain. Therefore the domain of ( p ∘ q ) is the set of all real numbers. The domain of q(x) = x + 3 is the set of all real numbers. The initial version of Theorem 1 appeared in 5, 7 where instead of cubical condensers there were considered more general condensers of the form E (F,U) in D ( USubset D is an open set and Fsubset U is a continuum).
The domain of p(x) = x 2 - 1 is the set of all real numbers. The equivalence of claims (1) (3) of Theorem 1 is proved in 6 for 1< qle p
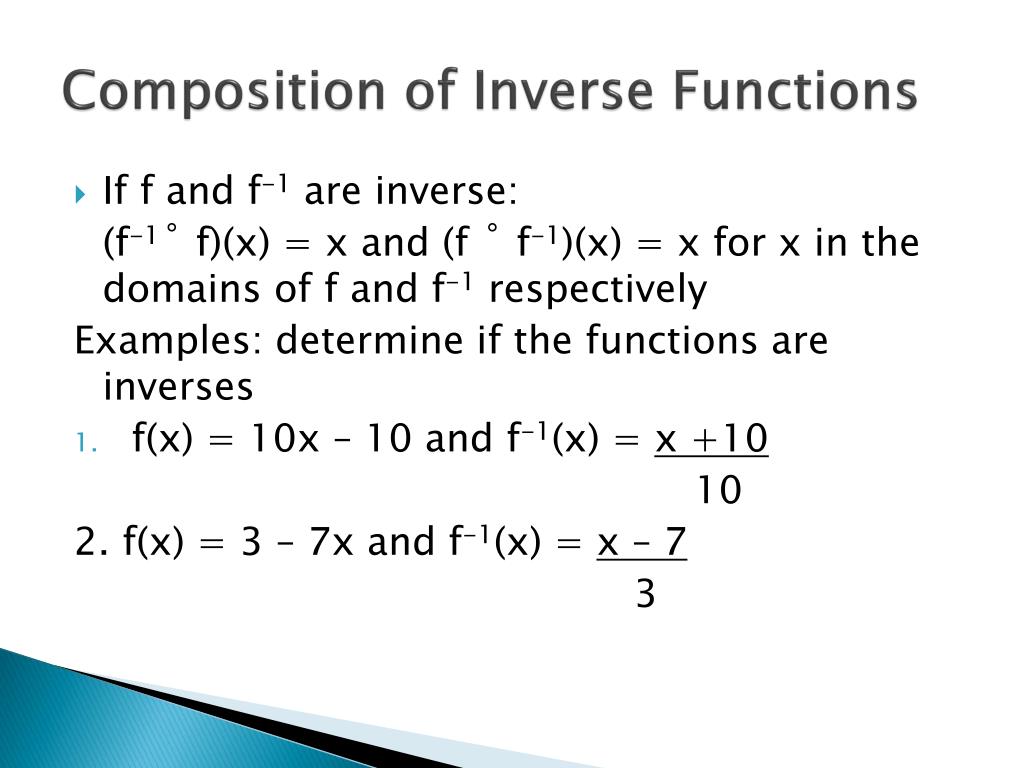
(This is the “outside” f, which is not continuous here.) This time, the limiting value, 2, is approached from both sides. Composite functions and Evaluating functions : f(x), g(x), fog(x), gof(x) Calculator - 1. Definition and Formula for Determining the Limit of Composite Functions. Now as we approach 0 from both sides approached from both sides. Step 3: Evaluate the outer function with the value that we found in step 1. To clarify this a little more, let’s look at a similar problem suggested by Sondra Edwards on the Facebook site: Consider this similar function: So we need to find the value of f as its argument approaches. But, notice that as x approaches 0 from both sides, the limit 2 is approached from the left (from below). In this video we learn about f(g(x)) and g. Composite functions are combinations of more than one function. Since f is not continuous at 2, the theorem cannot be used. In this video we learn about function composition. Given the graph of a function f, shown at the left, what is ? In this form the limit is obviously 3.Įxample 2: The second example is also based on a graph. Although we cannot be certain, it appears that. Therefore, as f approaches 1 from the leftĪnother approach is to try to write the equation of f.
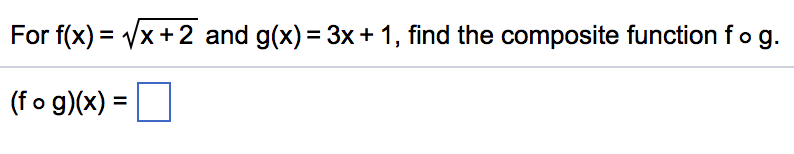
Stay on top of important topics and build connections by joining Wolfram. However, on closer examination, we see that is always less than 1, so is approaching 1 from the left (or from below). Wolfram Community forum discussion about Solve equations for composite functions. Īt first glance it appears that as x approaches zero, approaches 1 and the limit does not exist since f is not continuous at 1, so the theorem cannot be used. Students were given the graph at the right and asked to find. Let’s look at some.Įxample 1:The first example is from the 2016 BC International exam, question 88. g (x) becomes the input of the other f (x). This does not mean that the limits necessarily do not exist, rather that we need to find some other way of determining them. Worksheets are Inverse of functions work, Work 1 precalculus review. The problem is that in the examples one or the other of the hypotheses (continuity or the existence of ) is not met. The theorem that we would like to apply in these cases is this: Recently, a number of questions about the limit of composite functions have been discussed on the AP Calculus Community bulletin board and also on the AP Calc TEACHERS – AB/BC Facebook page.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
